What is dental zirconia?
Dental zirconia is zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), which is a crystalline oxide of metallic zirconium.
Zirconia restorations are made of this crystalline oxide form of zirconium and are considered to be ceramic restorations and not metal (like gold, silver, or porcelain fused to metal crowns).
Need a local dentist?
Is zirconia metal-free?
Yes, zirconia is considered to be metal-free.
Although zirconium is a metal, its oxide, zirconium dioxide - usually called zirconia - has a very different crystal structure and physical properties.
Even though there are metallic atoms in the crystal, the structure is never referred to as metal. Think of sodium, which is a metal, but sodium chloride - commonly known as salt - is not a metal.
Since the 1960s, zirconia has had various medical uses. It is extremely durable and 100% biocompatible. Zirconia is used for various prostheses in surgeries on the hip, finger, and ear.
Despite not being a metal, zirconia restorations are the strongest dental restorations, zirconia is so strong that it is even called "ceramic steel".
Since the 1990s, zirconia has been used for endodontic posts and implants too. (Endodontic post helps you retain your restorations and fillings as well as crowns.)
Why is zirconia used in dentistry?
Zirconia is one of the materials highly recommended by dentists because of its strength, longevity, and biocompatibility.
Comparing it to porcelain or composites, it is more fracture and chip-resistant, stiffer, and can handle higher loads of chewing pressure. It is known to hold a flexural strength of more than 900MPa.
Zirconia also masks the underneath structure because it is opaque and dull white. This makes it more esthetically pleasing since it mimics the color of a natural tooth.
Zirconia is also the superior choice if the patient is allergic to certain metals. It is biocompatible because it eliminates the possibility of the body having a reaction or immunological response like inflammation.
How is zirconia used by dentists?
One of the most popular uses of zirconia in dentistry is for crowns and bridges. Zirconia is often used for metal-free fixed partial dentures or single tooth reconstructions.
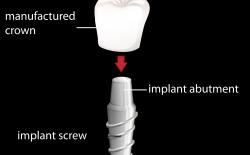
Zirconia is also used in implant dentistry as a dental implant for several reasons:
-
It does not inhibit osteoblasts, which are essential for osseointegration.
-
Even though titanium integrates better with the bone, zirconia is often the choice in situations where dentists are treating anterior teeth.
-
Titanium implants tend to have a gray discoloration that causes an unfavorable esthetic result.
-
Titanium might also exhibit corrosive reactions which cause complications in the tissues and the oral environment.
Due to these issues, zirconium-based posts were developed by dentists and it resulted in a more esthetically pleasing and biocompatible outcome.
Zirconia is also used as an implant abutment. With the toughness of zirconia and lower modulus of elasticity, it provides a solution of titanium (traditional material for implant abutment) brittleness which decreases the possibility of implant failure.
Zirconia abutments provide:
-
tooth color match
-
good tissue compatibility
-
lower plaque accumulation
Types of zirconia
There are three types of zirconia: solid, high translucent, and layered. All of them can be made using CAD-CAM technology.
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design and CAM stands for Computer-Aided Manufacturing. These technologies give you a precise fit and unmatchable look.
Solid zirconia
-
As the name suggests solid zirconia is tougher compared to high translucent zirconia. It can withstand chewing forces as well as bruxism forces better.
-
Solid zirconia also suits root canal-treated teeth, by offering stronger support for the weak teeth.
-
As it’s opaque, it’s more suited for posterior/back teeth.
High translucent zirconia
-
This type of zirconia gives you a superior look that exactly resembles your natural teeth. It is more suited for anterior/front teeth.
-
Its strength is higher than porcelain fused to metal crowns.
-
If you need extensive orthodontic treatment to correct the alignment of your teeth, your dentist may not prefer high translucent zirconia.
Layered zirconia
-
Unlike solid zirconia, it is more suitable when treating the anterior region because it is more translucent and opalescent.
-
It consists of zirconia inside and is covered with a layer of porcelain outside. Although it is still durable, the porcelain layer of the layered zirconia is often fragile. It is not recommended to use it with a forceful large bite.
-
These are more esthetic because they are hand-created. Skillful technicians easily create shapes, color match, and add details that resemble a natural tooth.
Need a local dentist?
Advantages of zirconia
Biocompatibility
Zirconia is highly biocompatible. The smooth surface helps to decrease plaque accumulation. It also promotes good tissue response as it is metal-free. It eliminates allergic reactions in patients who have metal allergies. It also prevents the darkening of the surrounding tissues.
Esthetics
Since it is custom-made for each patient, it lessens the margin of error and ensures a perfect fit.
It is also translucent so it can transmit the color of the adjacent teeth. It can also be manufactured in a wide variety of shades which makes it easier to color match the patient’s remaining natural teeth.
Strength
Zirconia is a very robust substance that does not have the bulkiness of typical porcelain. It is difficult to fracture or break due to its resilience to wear. It is practically unbreakable and stands up to bruxism and parafunctional habits better than any other material now available since it has higher fracture resistance than other dental materials.
Problems with zirconia
Tooth reduction
When opposed to the minimal reduction of ceramic glass materials, a zirconia crown disadvantage could be a more aggressive tooth reduction to produce strength and an aesthetic outcome. Following the original tooth anatomy, zirconia crowns require a minimal marginal depth of 0.6 mm, an axial wall reduction of at least 1.0 mm, and an occlusal reduction of 1.5 mm.
Cost
Zirconia crowns are usually as expensive as or more expensive than other forms of dental crowns. In the United States, zirconia crowns cost between $1,000 and $2,500 per crown, depending on the case's difficulty.
You might also be interested in:
Zirconia Dental Implants
Rare allergic reactions or aesthetic reasons can sometimes indicate a zirconia implant instead of titanium. Zirconia implants are relatively new but look very promising.
Zirconia Bridges
Zirconia is a very durable material, suitable for making long span bridges. It also looks very natural.
Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns are getting popular. Great durability, great esthetics, and an acceptable price.