Usage of gold in dentistry
While most people don't prefer gold restorations because of their low esthetic appeal, others are specifically looking for a gold tooth.
Many dentists like gold, as it has a lot of great properties:
- Long-lasting: Gold restorations are extremely durable, gold crowns and bridges with the proper oral hygiene can last for decades.
- Superior corrosion resistance: Gold is a high-noble metal (non-reactive), it does not react with the body fluids, and with the food you eat. However, there are some studies that debate this and found that gold restorations can increase gold sensitivity and are not completely inert.
- Fits perfectly: Dental technicians also like gold, as it's easy to work with it and even if the dentist needs to make smaller adjustments while fitting the crown or bridge, it's usually possible to do it.
- Tooth saving: Because of the durability and easy fitting, very little tooth structure needs to be removed when the restoration is made of gold.
- Friendly to the opposing teeth: Ceramic crowns are so tough that they tend to wear out the opposing teeth. This is usually not a problem with gold. Actually, gold restorations are recommended for patients with bruxism.
- Little chance of allergic reactions: Your body tolerates gold better than most other metals, allergic reactions are rare.
- Does not crack or chip: When you eat or drink something cold/hot, your teeth respond to that with contraction/expansion. The good thing about gold is that its response to temperature changes is very similar to your teeth, which makes gold restoration less likely to crack or chip.
Despite the many advantages, gold is just not suitable for dental implants. If you want to replace a missing tooth with a gold tooth implant, it's not a gold implant that you'll get, but a titanium implant (maybe zirconia) with a gold crown.
A short video about the advantages of gold in dentistry. Duration: 1:34.
Why gold is not suitable for dental implants?
Most dentists prefer gold for restorations as gold has excellent corrosion resistance and high biocompatibility (small chance of allergic reactions), fits perfectly, and lasts long.
However, there are a few more criteria that prevent gold from being used to manufacture implants.
Osseointegration problems
Tooth implants are placed inside the jaw bone and left in place, to allow the bone to adapt to the surface of the implant. This process is called osseointegration. This takes a period of 4-6 months depending upon the density and the quality of the bone.
Osseointegration is the most important thing required for the clinical success of a dental implant. Failure of it leads to a poor anchorage that causes loosening of the implant and implant failure.
Gold does not show osseointegration to the extent required for the clinical success of the implant.
Toughness
Toughness is another important property of dental implants.
The implant has to withstand masticatory load (stresses generated while chewing) so that the restoration (crown or bridge) stays firmly in its place.
Compared to other materials used in implants, gold is softer. Even though gold can be alloyed with other metals, like copper, which increases its strength, it still does not meet the required toughness for implants.
Despite the many other properties of gold that are favorable, the problems with osseointegration and toughness prevent gold from being used for dental implants.
What materials are used for dental implants?
Metal: Titanium and titanium alloys (with aluminum and vanadium) are most commonly used among the metals. They have excellent biocompatibility and resonate well with living tissues in the body. Titanium implants are surface treated to achieve more stable and favorable results. The surface treatment with sandblasting and acid etching have greatly increased the clinical success rates of titanium implants.
Ceramic: Ceramics is now used widely under clinical practice and the trend is progressively increasing now with time. The most commonly used ceramic is zirconia (zirconium dioxide). The main reason is its structural modification which makes it resistant to crack propagation. This improves the success rates of this material. Also, it is a metal-free material, a crystalline substance that can be used in patients who are allergic to metals.
Polymer: This group contains composite materials. They are not used often as implants but they are widely used as a restorative material and also for making artificial crowns.
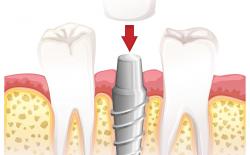
Structure of a dental implant restoration
The basic structure of an implant restoration has 3 components:
- The screw or implant: This part is placed inside the jaw bone surgically. It is an artificial root that holds the entire restoration in place, just like a natural root that holds the tooth. This part is not visible as it's inside your bone, beneath the gums. In radiographs, it can be clearly differentiated from natural roots as a radio-opaque component.
- The abutment: The abutment is fitted inside the screw. It does not penetrate the entire length of the screw but just a few millimeters to obtain a close grip and lock to stay in place. This actually serves the purpose of a prepared (trimmed) natural tooth to receive a crown on it. The abutment is partially inside the gums and the upper half is visible in the mouth. It is made of titanium or zirconia.
- The crown or bridge: The crown is placed on the abutment. Once the restoration is finished, only the crown will be visible. Crowns can be ceramic or metal, like gold.
When a missing tooth is replaced with gold, the third component - the crown - can be gold, the implant, and more often than not the abutment is not gold.
How much does a permanent tooth with a gold crown cost?
A typical single tooth replacement with dental implants costs around $3,000 and $5,000.
When you are getting a gold tooth, you are paying for a traditional dental implant (titanium or zirconia) and a gold dental crown. Since gold crowns are relatively expensive, the cost of the entire tooth restoration might be closer to the higher end.
Cost varies depending on the price of gold and also on its purity, your dentist fees, any additional treatments you might need.
Need a local dentist?
Types of gold crowns
So as discussed above, a gold tooth restoration usually consists of a titanium dental implant and abutment with a gold crown.
These are the common types of gold crowns:
Full coverage gold crown: They can be from pure gold or gold alloys. Gold alloys are preferred to improve the strength and the properties of the metal and also to make it economical. The wax build-up is made on the cast which is then cast with gold. The gold crown is then polished and finished. The crown is adjusted to obtain a close fit and proper teeth contacts on closure and on functional movements. It is then cemented to the tooth or the implant abutment.
Porcelain fused to gold (PFG): Porcelain fused to gold is like conventional porcelain fused to metal (PFM). Only the metal portion used here is gold. The inner layer of the crown is gold and the outer layer is porcelain, which makes this crown a lot more esthetic than a pure gold crown.
Partial crowns: This includes three forth crowns, reverse three forth crowns, etc. This can be prepared from pure gold or gold alloys like full coverage gold crowns.
You might also be interested in:
Dental Implant Costs
Tooth implants are quite expensive, a single tooth restoration (crowns included) can be around $3,000 and $5.000. Read our article to find out what factors affect the price of an implant.
Dental Implant Failure
The success rate of dental implants is around 95%-98%, so sometimes they do fail. Find out the most common causes of dental implant failure!
Full Mouth Dental Implants
This is the most complex and most expensive implant procedure. Learn more about the procedure, the prices, and the pros and cons.